What are lecture notes on severe malaria?
Severe Malaria: A Threatening Complication
1. Definition and Cause:
- Severe malaria is a life-threatening complication arising from Plasmodium parasite infection, most commonly Plasmodium falciparum.
- It's a progression from untreated or delayed treatment of uncomplicated malaria.
- Nearly all severe malaria deaths are linked to P. falciparum.
2. Pathogenesis:
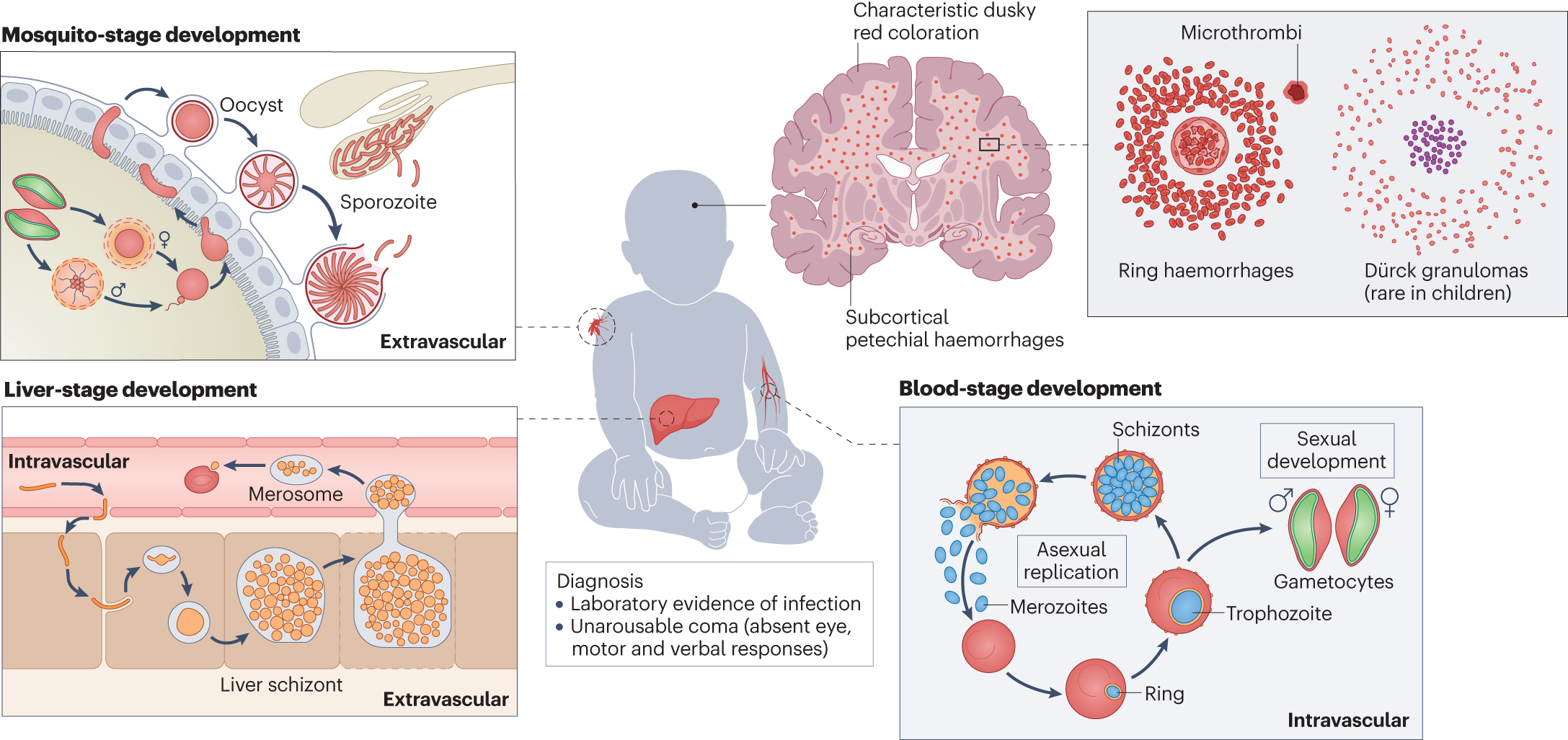
- The hallmark of severe malaria is vital organ dysfunction.
- Infected red blood cells (RBCs) clump together, blocking capillaries and reducing blood flow to organs.
- This blockage and parasite rupture release toxins, further damaging tissues.
- Cytokine release (immune response chemicals) might also play a role, though the exact mechanism remains unclear.
3. Clinical Features:
- Severe malaria presents with various signs and symptoms beyond typical malaria.
- Look out for:
- Impaired consciousness (confusion, coma)
- Severe anemia
- Respiratory distress
- Kidney failure
- Low blood sugar
- Bleeding problems
- Seizures
4. Diagnosis:
- Rapid diagnosis is crucial for prompt treatment and improved outcomes.
- Microscopic examination of blood smears remains the gold standard for parasite detection.
- Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are becoming increasingly used for quick diagnosis in resource-limited settings.
5. Treatment:
- Severe malaria is a medical emergency requiring hospitalization and intensive care.
- Antimalarial medications are the mainstay of treatment, with specific drugs depending on parasite type and local resistance patterns.
- Supportive care focuses on managing complications like anemia, electrolyte imbalances, and organ dysfunction.
6. Importance of Early Treatment:
- Early diagnosis and treatment of uncomplicated malaria significantly reduce the risk of progression to severe malaria.
- Public health efforts focus on malaria prevention through mosquito control and chemoprophylaxis for travelers visiting endemic areas.
7. Conclusion:
- Severe malaria is a preventable and treatable complication, but prompt diagnosis and intervention are essential for good outcomes.
- Understanding the pathogenesis and clinical features helps healthcare providers recognize and manage this life-threatening condition.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks